![]()
History
The First St Louis was laid down on 12
February 1827;
launched on 18 August 1828; and commissioned
on 20
December 1828, Master Commandant John
D. Sloat in command.
Ironclad

![]()
History
The First St Louis was laid down on 12
February 1827;
launched on 18 August 1828; and commissioned
on 20
December 1828, Master Commandant John
D. Sloat in command.
Ironclad

The first Eads ironclad gunboat was named St
Louis. In Early 1862 she was made
flagship by Admiral Foote for the fight against Fort Donelson. March
16th, with the
USS Benton lashed between the St Louis
and the USS Cincinnati, the upper battery of Island No. 10 was engaged.
The St Louis took a gunburst killing 2, wounding 13. In early June,
the St Louis played a part in the battle for Memphis. 17 June, the St Louis
was involved in the attack of the Southern Batteries in St
Charles, Arkansas- it was a Union victory. In October of 1862, she
was renamed Baron DeKalb.
Spanish American War St. Louis

Launched on 12 November 1894 and entered merchant service in 1895. She was commissioned as an auxiliary cruiser in the United States Navy on 24 April 1898 for the Spanish American War. The St Louis was specially outfitted with heavy drag lines in order to destroy undersea cable communications in the West Indies and to the mainland of South America.Decommissioned on 2 September 1898 and was turned over to Mr. J. Parker, a representative of the American Lines. For many years, SS St Louis was prominent as a passenger liner between New York and Liverpool. On 17 April 1918, St Louis was delivered to the Navy at New York to be wholly manned and operated by the Navy as a troop transport. She was renamed Louisville (SP-1644), as a cruiser named St Louis was already in service in the Navy. Louisville was commissioned on 24 April. decommissioned there on 9 September 1919. She was returned to her owner on the 11th and resumed her original name, St Louis. Scrapped in 1925.
C-20 CA-18
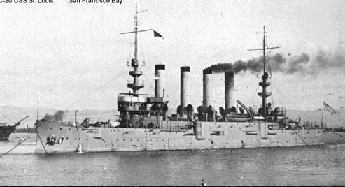
USS St Louis, [(Cruiser # 20, C-20, later CA-18),
1906-1930] a 9700-ton built at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, was commissioned
in August 1906. After a brief period in the Atlantic, she was assigned
to the Pacific Fleet, arriving there in mid-1907. For the next
decade, Saint Louis served as a training, receiving and submarine
support ship, as well as in traditional cruiser roles
along the U.S. west Coast, at Pearl Harbor
and elsewhere in the eastern Pacific. In 1917, with the U.S. entry
into World War I, St Louis was transferred to the Atlantic, where she served
as a transport and escorted convoys. Following the Armistice, she brought
home thousands of U.S. troops from Europe. Redesignated CA-18 in July 1920,
she was sent to the Mediterranean
during a period of great turmoil in Turkey.
Returning to the United States late in 1921, Saint Louis
decommissioned in March 1922. After eight
years in reserve, she was sold for scrap in August 1930.
CL-49
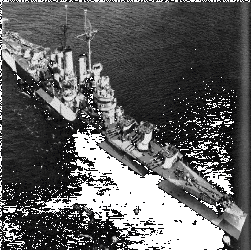
CL-49
Displacement: 10,000 t.
Length: 608’4”
Beam: 61’8”
Draft: 19’10”
Speed: 33 k.
Complement: 888
Armament: 15 6”; 8 5”; 16 1.1”; 12 20mm;
1 depth charge track
Class: St Louis
The fifth St Louis (CL-49) was laid down on
10 December 1936 by the Newport News
Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Co., Newport News,
Va.; commissioned on 19 May 1939, Capt. Charles H. Morrison in command.
She was at Pearl Harbor on the fateful day
in December 1941 when the Japanese attacked. She was not sunk
there at Pearl Harbor. February 14, 1944 The cruiser was damaged
by a dive bomber in the Bismarch Archipelago. St Louis earned eleven battle
stars during World War II. She was decommissioned on 20 June 1946.
Her name was struck from the Navy list on 22 January 1951, and, on
the 29th, she was commissioned in the Brazilian Navy as Tamandare.
